Bursitis In The Foot
Heel pain can also be caused due a condition called Bursitis which is constant irritation of the heel's natural cushion (bursa). This can lead to additional pain at the back of the heel when the ankle is moved and there may be swelling on both sides of the Achilles tendon. Useful treatments for Heel bursitis are anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin and Ibuprofen gel/tablets. Cold ice-pack compresses can be useful in reducing any swelling. In conjunction to these treatments it is important to stabalise and protect the heel. Gel heel pads will help to let the inflamed bursa settle down, however in severe chronic cases sometimes the use of Cortisone injections may be indicated.
Causes
The most common causative organism is Staphylococcus aureus (80% of cases), followed by streptococci. However, many other organisms have been implicated in septic bursitis, including mycobacteria (both tuberculous and nontuberculous strains), fungi (Candida), and algae (Prototheca wickerhamii). Factors predisposing to infection include diabetes mellitus, steroid therapy, uremia, alcoholism, skin disease, and trauma. A history of noninfectious inflammation of the bursa also increases the risk of septic bursitis.
Symptoms
Pain and tenderness usually develop slowly over time. Applying pressure to the back of the heel can cause pain. Wearing shoes may become uncomfortable. The back of the heel may feel achy. Pain is exacerbated when the foot is pointed or flexed, because the swollen bursa can get squeezed. A person with retrocalcaneal bursitis may feel pain when standing on their toes. Fever or chills in addition to other bursitis symptoms can be a sign of septic bursitis. Though uncommon, septic retrocalcaneal bursitis is a serious condition, and patients should seek medical care to ensure the infection does not spread.
Diagnosis
Bursitis is usually diagnosed after a careful physical examination and a full review of your medical history. If you garden and spend a lot of time on your knees, or if you have rheumatoid arthritis, tell your doctor, this information can be very helpful. During the physical exam, he or she will press on different spots around the joint that hurts. The goal is to locate the specific bursa that is causing the problem. The doctor will also test your range of motion in the affected joint. Other tests usually aren?t required to diagnose bursitis, but your doctor may suggest an MRI, X-ray or ultrasound to rule out other potential causes of pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Your health care provider may recommend the following treatments. Avoid activities that cause pain. Ice the heel several times a day. Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (for example, ibuprofen). Try over-the-counter or custom heel wedges to help decrease the stress on the heel. Try ultrasound treatment during physical therapy to reduce inflammation. Use physical therapy to improve flexibility and strength around the ankle, which can help the bursitis improve and prevent it from coming back. If these treatments don't work, your health care provider may inject a small amount of steroids into the bursa. After the injection, you should avoid stretching the tendon too much because it can break open (rupture). If the condition is connected with Achilles tendinitis, casting the ankle for several weeks to keep it from moving can be effective. Very rarely, surgery may be needed to remove the inflamed bursa.
Surgical Treatment
Only if non-surgical attempts at treatment fail, will it make sense to consider surgery. Surgery for retrocalcanel bursitis can include many different procedures. Some of these include removal of the bursa, removing any excess bone at the back of the heel (calcaneal exostectomy), and occasionally detachment and re-attachment of the Achilles tendon. If the foot structure and shape of the heel bone is a primary cause of the bursitis, surgery to re-align the heel bone (calcaneal osteotomy) may be considered. Regardless of which exact surgery is planned, the goal is always to decrease pain and correct the deformity. The idea is to get you back to the activities that you really enjoy. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the exact surgical procedure that is most likely to correct the problem in your case. But if you have to have surgery, you can work together to develop a plan that will help assure success.
Can Cortisone Decrease Hammer Toe Pain
 Overview
Overview
A hammertoe is a toe that is bent because of a weakened muscle. The weakened muscle makes the tendons (tissues that connect muscles to bone) shorter, causing the toes to curl under the feet. Hammertoes can run in families. They can also be caused by shoes that are too short. Hammertoes can cause problems with walking and can lead to other foot problems, such as blisters, calluses, and sores. Splinting and corrective footwear can help in treating hammertoes. In severe cases, surgery to straighten the toe may be necessary.
Causes
Most hammertoes are caused by wearing ill-fitting, tight or high-heeled shoes over a long period of time. Shoes that don?t fit well can crowd the toes, putting pressure on the middle toes and causing them to curl downward. Other causes include genes. Some people are born with hammertoe, bunions. These knobby bumps sometimes develop at the side of the big toe. This can make the big toe bend toward the other toes. The big toe can then overlap and crowd the smaller toes. Arthritis in a toe joint can lead to hammertoe.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
People with a hammer toe will often find that a corn or callus will develop on the top of the toe, where it rubs against the top of the footwear. This can be hammertoe painful when pressure is applied or when anything rubs on it. The affected joint may also be painful and appear swollen.
Diagnosis
A hammertoe is usually diagnosed with a physical inspection of your toe. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, may be ordered if you have had a bone, muscle, or ligament injury in your toe.
Non Surgical Treatment
If your toe is still flexible, your doctor may recommend that you change to roomier and more comfortable footwear and that you wear shoe inserts (orthotics) or pads. Wearing inserts or pads can reposition your toe and relieve pressure and pain. In addition, your doctor may suggest exercises to stretch and strengthen your toe muscles. These may include picking up marbles or a thin towel off the floor with your toes.
Surgical Treatment
For the surgical correction of a rigid hammertoe, the surgical procedure consists of removing the damaged skin where the corn is located. Then a small section of bone is removed at the level of the rigid joint. The sutures remain in place for approximately ten days. During this period of time it is important to keep the area dry. Most surgeons prefer to leave the bandage in place until the patient's follow-up visit, so there is no need for the patient to change the bandages at home. The patient is returned to a stiff-soled walking shoe in about two weeks. It is important to try and stay off the foot as much as possible during this time. Excessive swelling of the toe is the most common patient complaint. In severe cases of hammertoe deformity a pin may be required to hold the toe in place and the surgeon may elect to fuse the bones in the toe. This requires several weeks of recovery.
Bunion Splint Effectiveness
Overview
 A bunion is a bony protrusion on the side of the big toe or in some less common cases on the outside of the small toe. The protrusion at the joint of the base of the toe can become irritated, swollen and painful. As the protrusion becomes larger the toe bends toward the second toe causing further sources of irritation. There appears to be multiple causes of a bunion. Genetically the foot may be shaped such that normal activity puts excessive pressure on the big toe eventually causing a bunion. Some suggest footwear that does not fit properly may also put excessive pressure and cause a bunion. The protrusion may be excessive bone structure or a fluid sac called the bursa that becomes inflamed. In any case the deformity of the toe makes it difficult to find proper fitting footwear, is not a pleasant sight, and can be very painful.
A bunion is a bony protrusion on the side of the big toe or in some less common cases on the outside of the small toe. The protrusion at the joint of the base of the toe can become irritated, swollen and painful. As the protrusion becomes larger the toe bends toward the second toe causing further sources of irritation. There appears to be multiple causes of a bunion. Genetically the foot may be shaped such that normal activity puts excessive pressure on the big toe eventually causing a bunion. Some suggest footwear that does not fit properly may also put excessive pressure and cause a bunion. The protrusion may be excessive bone structure or a fluid sac called the bursa that becomes inflamed. In any case the deformity of the toe makes it difficult to find proper fitting footwear, is not a pleasant sight, and can be very painful.
Causes
With prolonged wearing of constraining footwear your toes will adapt to the new position and lead to the deformity we know as a foot bunion. Footwear is not the only cause of a bunion. Injuries to the foot can also be a factor in developing a bunion. Poor foot arch control leading to flat feet or foot overpronation does make you biomechanically susceptible to foot bunions. A family history of bunions also increases your likelihood of developing bunions. Many people who have a bunion have a combination of factors that makes them susceptible to having this condition. For example, if you are a women over the age of forty with a family history of bunions, and often wear high-heeled shoes, you would be considered highly likely to develop a bunion.
Symptoms
Patients with bunions will often display pain over the prominent bump on the inside of their forefoot (the medial eminence?). However, they may also have pain under the ball of the foot (under the area near the base of the second toe). Symptoms can vary in severity from none at all to severe discomfort aggravated by standing and walking. There is no direct correlation between the size of the bunion and the patient?s symptoms. Some patients with severe bunion deformities have minimal symptoms, while patients with mild bunion deformities may have significant symptoms. Symptoms are often exacerbated by restrictive shoe wear, particularly shoes with a narrow toe box or an uncomfortable, stiff, restraining upper.
Diagnosis
People with bunions may be concerned about the changing appearance of their feet, but it is usually the pain caused by the condition that leads them to consult their doctor. The doctor will evaluate any symptoms experienced and examine the affected foot for joint enlargement, tissue swelling and/or tenderness. They will also assess any risk factors for the condition and will ask about family history. An x-ray of the foot is usually recommended so that the alignment of big toe joint can be assessed. This would also allow any other conditions that may be affecting the joint, such as arthritis, to be seen.
Non Surgical Treatment
Follow the advice given by a Podiatrist. Use felt pads to help keep pressure off the painful area of the bunions. Wear shoes that are wide and deep to accomodate the bunions. Fitting of footwear is very important. Avoid the use of high heel shoes. Use exercises to keep the joint mobile. Night splints may help with the bunion symptoms. The aim of these are to hold the toe in a more correct position. Padding or foam between the big toe and the second toe is sometimes recommended, it should, generally, not be recommended as the big toe is usually so strong it just further 'squeezes' the lesser toes and can lead to problems between these toes. The padding between the two toes will not straighten the big toe. However, sometimes the padding may be needed to help with symptoms that originate inside the joint if the bunion is painful. 
Surgical Treatment
In severe hallux valgus bunion cases, the first long bone (metatarsal) in the foot dramatically shifts away from the second metatarsal, resulting in looseness and a large deformity. In severe bunion corrections, a surgery known as the Lapidus procedure realigns the first metatarsal into its natural position. Using screws, the surgery holds the bone stable so it does not shift again and reduces the change of the bunion returning to basically none. Surgery may also involve removing the enlarged portion of the bunion region, cutting and realigning the bone, and correcting the position of the tendons and ligaments. By using a special plate with Lapidus procedures, University Foot and Ankle Institute patients are able to put weight on their foot after only 2-3 weeks, rather than the typical 6-8 weeks of no weight.
Prevention
To help prevent bunions be sure your shoes don't cramp or irritate your toes. Choose shoes with a wide toe box - there should be space between the tip of your longest toe and the end of the shoe. Your shoes should conform to the shape of your feet without squeezing or pressing any part of your foot. Avoid pointy-toed shoes.
Understand More About Overpronation
Pronation, in anatomical terms, means to rotate, and it applies to any rotational movement of a bone. Pronation in the feet involves an inward rolling of the foot throughout the gait which helps with the transfer of force. Normally the foot will move from the heel to the toes with only a small degree of pronation, with a slight inward roll from the outside of the heel to the inside of the foot which helps to support the body weight. Normal pronation involves the rolling of the foot to approximately 15 degrees. If you have normal foot arches, you are likely to be a neutral runner and will most likely pronate normally.

Causes
There are many biomechanical issues that can contribute to excessive pronation, including weak foot intrinsic muscles, limited ankle dorsiflexion mobility and calf flexibility, weak ankle invertor muscles (e.g. posterior tibialis), weak forefoot evertor muscles (peroneus longus), poor hip strength and control, Anterior pelvic tilting, heel InversionIn a person who overpronates, the heel bone goes into an everted position meaning that it turns out away from the midline of the body. The opposite motion of eversion is inversion. Inversion is a motion that needs to be controlled to prevent the foot from excessively pronating.
Symptoms
People with overpronation may suffer from pain in the knees, hips, and low back. Overpronation itself does not necessarily cause any other symptoms but is a contributing factor of many foot conditions such as Plantar Facsiitis, Heel Spur Syndrome, Posterior Tibialis Tendon Rupture or Tendonitis, Hallux Valgus, Bunion Deformities, Metatarsalgia, Hallux Limitus or Hallux Rigidus, Hammer Toes, and Morton?s Neuroma.
Diagnosis
So, how can you tell if you have overpronation, or abnormal motion in your feet, and what plantar fasciitis treatment will work to correct it? Look at your feet. While standing, do you clearly see the arch on the inside of your foot? If not, and if the innermost part of your sole touches the floor, then your feet are overpronated. Look at your (running/walking) shoes. If your shoes are more worn on the inside of the sole in particular, then pronation may be a problem for you. Use the wet foot test. Wet your feet and walk along a section of pavement, then look at the footprints you leave behind. A normal foot will leave a print of the heel connected to the forefoot by a strip approximately half the width of the foot on the outside of the sole. If you?re feet are pronated there may be little distinction between the rear and forefoot.

Non Surgical Treatment
Overpronation of the feet can be corrected in some cases and in others it can be effectively managed. Overpronators can train themselves to change their running gait, wear arch supports, orthotic insoles or specialist shoes for overpronators. In order to determine exactly what is happening during the stride, it is necessary to have a gait analysis conducted by a professional. The extent of overpronation can then be determined, and the causes can be identified and corrected directly. The main corrective methods used for excessive pronation are orthotics. Orthotics are the most straightforward and simplest solution to overpronation. Orthotics are devices which can be slipped into shoes which will offer varying degrees of correction to the motion of the foot. Orthotics help to support the arches and distribute the body weight effectively, and are usually the best treatment choice for moderate to severe overpronation. Orthotics may require existing insoles to be removed from your shoes to accommodate them; although most running shoes will have a removable insole to accommodate an orthotic insole.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. The ankle and hindfoot bones/midfoot bones around the joint are fused, locking the bones in place and preventing all joint motion. This may also be done in combination with fusion at other joints. This is a very aggressive option usually reserved for extreme cases where no joint flexibility is present and/or the patient has severe arthritic changes in the joint.
Diagnosing Calcaneal Apophysitis
Pain in the heel of a child's foot, typically brought on by some form of injury or trauma, is sometimes Sever's Disease. The disease often mimics Achilles tendonitis, an inflammation of the tendon attached to the back of the heel. A tight Achilles tendon may contribute to Sever's Disease by pulling excessively on the growth plate of the heel bone. This condition is most common in younger children and is frequently seen in the active soccer, football or baseball player. Sport shoes with cleats are also known to aggravate the condition. Treatment includes calf muscle stretching exercises, heel cushions in the shoes, and/or anti-inflammatory medications. Consult your physician before taking any medications.
Causes
Sever?s disease is common, and typically occurs during a child?s growth spurt, which can occur between the ages of 10 and 15 in boys and between the ages of 8 and 13 in girls. Feet tend to grow more quickly than other parts of the body, and in most kids the heel has finished growing by the age of 15. Being active in sports or participating in an activity that requires standing for long periods can increase the risk of developing Sever?s disease. In some cases, Sever?s disease first becomes apparent after a child begins a new sport, or when a new sports season starts. Sports that are commonly associated with Sever?s disease include track, basketball, soccer, and gymnastics. Children who are overweight or obese are also at a greater risk of developing this condition. Certain foot problems can also increase the risk, including. Over pronating. Kids who over pronate (roll the foot inward) when walking may develop Sever?s disease. Flat foot or high arch. An arch that is too high or too low can put more stress on the foot and the heel, and increase the risk of Sever?s disease. Short leg. Children who have one leg that is shorter than the other may experience Sever?s disease in the foot of the shorter leg because that foot is under more stress when walking.
Symptoms
Symptoms include complaints of pain or tenderness in the heel (or heels), discomfort when heel is squeezed, limping, and more severe pain after walking, running or playing sports. Sever?s disease is directly related to overuse of the bone and tendons in the heel. This can come from playing sports or anything that involves lots of heel movements and hard shoes such as cleats. It can be associated with starting a new sport, or the start of a new season. It occurs more commonly in children who pronate (feet roll inward), and involves both heels in more than half of patients.
Diagnosis
A doctor can usually tell that a child has Sever's disease based on the symptoms reported. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will probably examine the heels and ask about the child's activity level and participation in sports. The doctor might also use the squeeze test, squeezing the back part of the heel from both sides at the same time to see if doing so causes pain. The doctor might also ask the child to stand on tiptoes to see if that position causes pain. Although imaging tests such as X-rays generally are not that helpful in diagnosing Sever's disease, some doctors order them to rule out other problems, such as fractures. Sever's disease cannot be seen on an X-ray.
Non Surgical Treatment
Initially, Sever?s Disease is treated with rest, anti-inflammatory medication and softer shoes. Ice followed by heat is a common practice and heel cup orthotics have worked wonders for our young patients in the past. It can take anywhere from a few weeks to a year for these growth plates to naturally close - at which point Sever?s Disease disappears. Even though the condition does heal on its own, athletes are encouraged to seek treatment, rather than push through the pain. Simply ?dealing with it? and continuing to play sports despite the injury could lead to an impaired gait, a strained hip or a knee injury. Stretches to strengthen the leg muscles, leg compression wraps and over-the-counter acetaminophen or ibuprofen are also recommended treatments. In very rare cases, a podiatrist may recommend wearing a cast for two to twelve weeks.
Exercise
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with Severs disease. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 1 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate, advanced and other exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head as far as you can go without pain and provided you feel no more than a mild to moderate stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free. Once you can perform 20 repetitions consistently without pain, the exercise can be progressed by gradually increasing the resistance of the band provided there is no increase in symptoms. Bridging. Begin this exercise lying on your back in the position demonstrated. Slowly lift your bottom pushing through your feet, until your knees, hips and shoulders are in a straight line. Tighten your bottom muscles (gluteals) as you do this. Hold for 2 seconds then slowly lower your bottom back down. Repeat 10 times provided the exercise is pain free.
Causes Acquired Flat Feet
Overview
Adult Acquired Flatfoot (Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction) is a painful, progressive deformity in adults. It results from a gradual stretch (attenuation) of the tibialis posterior tendon and the ligaments that support your foot?s arch. This stretching causes the tendon to lose strength and function. Many people have flat feet and do not experience pain. However, pain occurs with Adult Acquired Flatfoot because the tendons and ligaments have been torn. Once the vital ligaments and posterior tibial tendon are lost, there is no longer anything holding the arch of the foot in place. 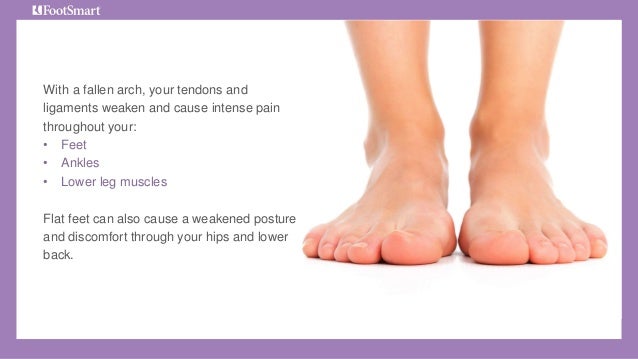
Causes
As the name suggests, adult-acquired flatfoot occurs once musculoskeletal maturity is reached, and it can present for a number of reasons, though one stands out among the others. While fractures, dislocations, tendon lacerations, and other such traumatic events do contribute to adult-acquired flatfoot as a significant lower extremity disorder, as mentioned above, damage to the posterior tibial tendon is most often at the heart of adult-acquired flatfoot. One study further elaborates on the matter by concluding that ?60% of patients [presenting with posterior tibial tendon damage and adult-acquired flatfoot] were obese or had diabetes mellitus, hypertension, previous surgery or trauma to the medial foot, or treatment with steroids?.
Symptoms
Many patients with this condition have no pain or symptoms. When problems do arise, the good news is that acquired flatfoot treatment is often very effective. Initially, it will be important to rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain.
Diagnosis
First, both feet should be examined with the patient standing and the entire lower extremity visible. The foot should be inspected from above as well as from behind the patient, as valgus angulation of the hindfoot is best appreciated when the foot is viewed from behind. Johnson described the so-called more-toes sign: with more advanced deformity and abduction of the forefoot, more of the lateral toes become visible when the foot is viewed from behind. The single-limb heel-rise test is an excellent determinant of the function of the posterior tibial tendon. The patient is asked to attempt to rise onto the ball of one foot while the other foot is suspended off the floor. Under normal circumstances, the posterior tibial muscle, which inverts and stabilizes the hindfoot, is activated as the patient begins to rise onto the forefoot. The gastrocnemius-soleus muscle group then elevates the calcaneus, and the heel-rise is accomplished. With dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, however, inversion of the heel is weak, and either the heel remains in valgus or the patient is unable to rise onto the forefoot. If the patient can do a single-limb heel-rise, the limb may be stressed further by asking the patient to perform this maneuver repetitively.
Non surgical Treatment
Conservative (nonoperative) care is advised at first. A simple modification to your shoe may be all that???s needed. Sometimes purchasing shoes with a good arch support is sufficient. For other patients, an off-the-shelf (prefabricated) shoe insert works well. The orthotic is designed specifically to position your foot in good alignment. Like the shoe insert, the orthotic fits inside the shoe. These work well for mild deformity or symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers or antiinflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen may be helpful. If symptoms are very severe, a removable boot or cast may be used to rest, support, and stabilize the foot and ankle while still allowing function. Patients with longer duration of symptoms or greater deformity may need a customized brace. The brace provides support and limits ankle motion. After several months, the brace is replaced with a foot orthotic. A physical therapy program of exercise to stretch and strengthen the foot and leg muscles is important. The therapist will also show you how to improve motor control and proprioception (joint sense of position). These added features help prevent and reduce injuries. 
Surgical Treatment
In cases where cast immobilization, orthoses and shoe therapy have failed, surgery is the next alternative. The goal of surgery and non-surgical treatment is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve mobility of the patient. Opinions vary as to the best surgical treatment for adult acquired flatfoot. Procedures commonly used to correct the condition include tendon debridement, tendon transfers, osteotomies (cutting and repositioning of bone) and joint fusions. (See surgical correction of adult acquired flatfoot). Patients with adult acquired flatfoot are advised to discuss thoroughly the benefits vs. risks of all surgical options. Most procedures have long-term recovery mandating that the correct procedure be utilized to give the best long-term benefit. Most flatfoot surgical procedures require six to twelve weeks of cast immobilization. Joint fusion procedures require eight weeks of non-weightbearing on the operated foot - meaning you will be on crutches for two months. The bottom line is, Make sure all of your non-surgical options have been covered before considering surgery. Your primary goals with any treatment are to eliminate pain and improve mobility. In many cases, with the properly designed foot orthosis or ankle brace, these goals can be achieved without surgical intervention.
What Are The Main Causes Of Adult Aquired Flat Feet ?
Adults with an acquired flatfoot deformity may present not with foot deformity but almost uniformly with medial foot pain and decreased function of the affected foot (for a list of causes of an acquired flatfoot deformity in adults. Patients whose acquired flatfoot is associated with a more generalised medical problem tend to receive their diagnosis and are referred appropriately. However, in patients whose adult acquired flatfoot deformity is a result of damage to the structures supporting the medial longitudinal arch, the diagnosis is often not made early. These patients are often otherwise healthier and tend to be relatively more affected by the loss of function resulting from an acquired flatfoot deformity. The most common cause of an acquired flatfoot deformity in an otherwise healthy adult is dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon, and this review provides an outline to its diagnosis and treatment.

Causes
As discussed above, many different problems can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to support the arch of your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot. This type of arthritis attacks not only the cartilage in the joints, but also the ligaments that support the foot. Inflammatory arthritis not only causes pain, but also causes the foot to change shape and become flat. The arthritis can affect the back of the foot or the middle of foot, both of which can result in a fallen arch. An injury to the tendons or ligaments in the foot can cause the joints to fall out of alignment. The ligaments support the bones and prevent them from moving. If the ligaments are torn, the foot will become flat and painful. This more commonly occurs in the middle of the foot (Lisfranc injury), but can also occur in the back of the foot. Injuries to tendons of the foot can occur either in one instance (traumatically) or with repeated use over time (overuse injury). Regardless of the cause, if tendon function is altered, the forces that are transmitted across joints in the foot are changed and this can lead to increased stress on joint cartilage and ligaments. In addition to tendon and ligament injuries, fractures and dislocations of the bones in the midfoot can also lead to a flatfoot deformity. People with diabetes or with nerve problems that limits normal feeling in the feet, can have collapse of the arch or of the entire foot. This type of arch collapse is typically more severe than that seen in patients with normal feeling in their feet. In addition to the ligaments not holding the bones in place, the bones themselves can sometimes fracture and disintegrate without the patient feeling any pain. This may result in a severely deformed foot that is very challenging to correct with surgery. Special shoes or braces are the best method for dealing with this problem.
Symptoms
The symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of the arch, and an inward rolling of the ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change. For example, when PTTD initially develops, there is pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the course of the tendon). In addition, the area may be red, warm, and swollen. Later, as the arch begins to flatten, there may still be pain on the inside of the foot and ankle. But at this point, the foot and toes begin to turn outward and the ankle rolls inward. As PTTD becomes more advanced, the arch flattens even more and the pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below the ankle. The tendon has deteriorated considerably and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Diagnosis
Looking at the patient when they stand will usually demonstrate a flatfoot deformity (marked flattening of the medial longitudinal arch). The front part of the foot (forefoot) is often splayed out to the side. This leads to the presence of a ?too many toes? sign. This sign is present when the toes can be seen from directly behind the patient. The gait is often somewhat flatfooted as the patient has the dysfunctional posterior tibial tendon can no longer stabilize the arch of the foot. The physician?s touch will often demonstrate tenderness and sometimes swelling over the inside of the ankle just below the bony prominence (the medial malleolus). There may also be pain in the outside aspect of the ankle. This pain originates from impingement or compression of two tendons between the outside ankle bone (fibula) and the heel bone (calcaneus) when the patient is standing.
Non surgical Treatment
This condition may be treated with conservative methods. These can include orthotic devices, special shoes, and bracing. Physical therapy, rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication may be prescribed to help relieve symptoms. If the condition is very severe, surgical treatment may be needed.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually performed when non-surgical measures have failed. The goal of surgery is to eliminate pain, stop progression of the deformity and improve a patient?s mobility. More than one technique may be used, and surgery tends to include one or more of the following. The tendon is reconstructed or replaced using another tendon in the foot or ankle The name of the technique depends on the tendon used. Flexor digitorum longus (FDL) transfer. Flexor hallucis longus (FHL) transfer. Tibialis anterior transfer (Cobb procedure). Calcaneal osteotomy - the heel bone may be shifted to bring your heel back under your leg and the position fixed with a screw. Lengthening of the Achilles tendon if it is particularly tight. Repair one of the ligaments under your foot. If you smoke, your surgeon may refuse to operate unless you can refrain from smoking before and during the healing phase of your procedure. Research has proven that smoking delays bone healing significantly.